Collagenous Sprue, Collagenous Gastritis, and an Uncommon Association with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Case Report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.52787/agl.v54i3.383Keywords:
Enteropathy, collagenous sprue, collagenous gastritis, collagenous enteritis, celiac disease, malabsorption, inflammatory bowel disease, chronic diarrheaAbstract
Celiac disease is the most common cause of intestinal villous atrophy. It may present with a clinical course characterized by chronic diarrhea, malabsorption, and weight loss. Diagnosis is based on the presence of positive specific antibodies in serum, characteristic enteropathy, and the clinical and histological response to a gluten-free diet. However, in some cases, patients with villous atrophy who do not respond to the exclusion of gluten from the diet present a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. It is essential to perform a differential diagnosis, as different pathologies can mimic celiac disease. The association of celiac disease with other immune-mediated diseases is well known, including inflammatory bowel disease. It is also frequently associated with microscopic colitis, which may be a potential cause of persistent or recurrent symptoms. The clinical course of celiac disease may be complicated by the development of additional conditions such as microscopic colitis, refractory celiac disease or collagenous sprue. Collagenous sprue is a rare enteropathy affecting the small intestine, characterized by the presence of villous atrophy and a thick band of subepithelial collagen. It may be associated with gastritis and lymphocytic and/or collagenous colitis. The literature describes its association with other autoimmune diseases. Complications may include ulceration, perforation, and the development of intestinal lymphoma. Consequently, it has high morbidity and mortality, and a poor prognosis. Knowledge about the natural history, pathogenesis and clinical evolution of collagenous sprue is limited. Some recent publications describe a benign course with a good response to treatment with immunosuppressants. However, the coexistence of celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease and collagenous sprue is rare, and is presented as isolated case reports.
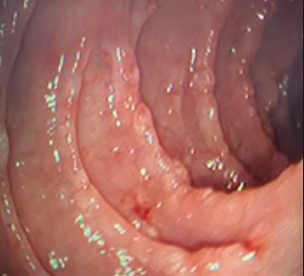
Case report. We present the case of a 52-year-old male patient diagnosed with collagenous gastroenteritis associated with inflammatory bowel disease, with unfavorable evolution despite treatment.
Conclusion. The report of additional cases of association between collagenous sprue and inflammatory bowel disease could help improve the clinical management of these patients.
References
-1. Kamboj AK., and Oxentenko AS. Clinical Review. Clinical and Histologic Mimickers of Celiac Disease. Clinical and Translational Gastroenterology (2017) 8, e114; DOI: 10.1038/ctg.2017.41. Official journal of the American College of Gastroenterology.
-2. HJ Freeman. Collagenous sprue. Can J Gastroenterol 2011;25(4):189-192.
-3. Gill I, Shaheen A A, Edhi A I, Amin M, Ketan Rana K, Cappell M S; Digestive Diseases and Sciences (2021) 66:4557-4564 Case Report. Novel Case Report: A Previously Reported, but Pathophysiologically Unexplained, Association Between Collagenous Colitis and Protein-Losing Enteropathy May Be Explained by an Undetected Link with Collagenous Duodenitis
-4. Freeman HJ. Refractory celiac disease and sprue-like intestinal disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2008 feb 14;14(6):828-30. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.828.
-5. Freeman, HJ. Review. Collagenous Sprue: A Distinctive and Heterogeneous Clinicopathologic Disorder. Gastroenterology & Hepatology Volume 5, Issue 6 June 2009.
-6. Vasant DH., Hayes S., Bucknall R., Lal S. Case Reports. Clinical and histological resolution of collagenous sprue following gluten-free diet and discontinuation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). BMJ Case Rep. 2013 Aug 28:2013: bcr2013200097. DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2013-200097.
-7. Soendergaard C, Riis LB, Nielsen OH. BMJ Case Rep 2014. Case Report. Collagenous sprue: a coeliac disease look-alike with different treatment strategy. DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2014-203721.
-8. Rubio-Tapia A., Nicholas J. Talley N. J., Gurudu S. R., Wu T. and Murray J. A. Gluten-Free Diet and Steroid Treatment Are Effective Therapy for Most Patients with Collagenous Sprue. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 April; 8(4): 344-349.e3.
-9. Xiangrong Zhao, Rebecca L. Johnson. Collagenous Sprue. A Rare, Severe Small-Bowel Malabsorptive Disorder. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011; 135:803-809
-10. Xiao Z, Vijaya M. Dasari VM, Kirby DF., Bronner M., Plesec TP., and Lashner BA. Collagenous Sprue: A Case Report and Literature Review. Gastroenterology & Hepatology Volume 5, Issue 6 June 2009.
-11. Evans MG., Guccione JP., Crymes A., Li X. Johnson CA., Chandan VS., and Lu Y. Case Report. Atypical Presentations of Collagenous Gastritis Mimicking Celiac Sprue. Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2023, Article ID 4073588, DOI: org/10.1155/2023/4073588.
-12. Freeman H J, Webber D L. Free perforation of the small intestine in collagenous sprue. World J Gastroenterol 2009 September 21;
(35): 4446-4448.
-13. Freeman HJ. Lymphoproliferative disorders in collagenous colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2005; 11: 781-782.
-14. Vakiani E., Arguelles-Grande C. Green P. H. et al. Collagenous sprue is not always associated with dismal outcomes: a clinicopathological study of 19 patients. Modern Pathology (2010) 23, 12-26; DOI: 10.1038/modpathol.2009.151.
-15. van Gils T, van de Donk T, Bouma G, et al. B The first cases of collagenous sprue successfully treated with thioguanine.
BMJ Open Gastro 2016; 3: e000099. DOI: 10.1136/bmjgast-2016-000099.
-16. Bhat S et al. Safety and Monitoring of inflammatory bowel disease Advanced therapies. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, 2023, XX, 1-5 17. Gordon H et al. ECCO Guidelines on Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Malignancies. Journal of Crohn's and Colitis, Volume 17, Issue 6, June 2023, Pages 827-854
-18. Sambuelli A y col. Manejo de la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal. revisión y algoritmos de tratamiento. Acta Gastroenterol Latinoam 2019;49(S2).
-19. Pinto-Sanchez MI, Seiler CL, Santesso N, et al. Association between inflammatory bowel diseases and celiac disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2020; 159:884-903.e31.
-20. Penny H.A, Baggus E.M.R, Rej A., Snowden J.A., Sanders D. S. Non-Responsive Coeliac Disease: A Comprehensive Review from the NHS England National Centre for Refractory Coeliac Disease. Nutrients 2020 Jan 14;12(1):216. DOI: 10.3390/nu12010216.
-21. Celiac disease, collagenous sprue and microscopic colitis in IBD. Observations from a population-based cohort of IBD (ICURE) Scand J Gastroenterol. 2015;50(10):1234-40. DOI: 10.3109/00365521.2015.1041152.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 María Laura Moreno

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.












